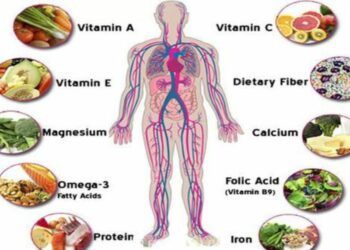
When it comes to maintaining a healthy diet, vitamins play a crucial role. They are essential nutrients that your body needs to function properly, support growth and development, and maintain good health. However, not all vitamins are created equal, and it’s important to understand the differences between them to ensure that you are getting the nutrients you need. In this article, we’ll explore the classification of vitamins into two categories: water-soluble and fat-soluble.
Understanding the Basics of Vitamins
Before we delve into the classification of vitamins, let’s start with some basics. Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for maintaining normal bodily functions. They are classified into two groups: fat-soluble and water-soluble. The main difference between these two types of vitamins is how they are absorbed and stored in the body.
Water-Soluble Vitamins
Water-soluble vitamins are those that dissolve in water and are not stored in the body for long periods. These vitamins include vitamin C and the B-complex vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, vitamin B6, folate, and vitamin B12). Since they are not stored in the body, excess amounts are excreted in the urine. Therefore, it’s essential to consume these vitamins regularly to ensure that you are getting enough.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins, on the other hand, are stored in the body’s fatty tissues and liver. These vitamins include vitamins A, D, E, and K. Since they are stored in the body, it’s possible to consume too much of these vitamins, which can lead to toxicity. However, deficiencies in these vitamins can also occur if your diet is lacking.
Identifying Water-Soluble Vitamins
One way to identify water-soluble vitamins is by their properties. Water-soluble vitamins are typically found in foods that have a high water content, such as fruits, vegetables, and grains. They are also easily destroyed by heat, so cooking methods such as boiling can reduce the vitamin content in these foods. Therefore, it’s essential to eat these foods raw or lightly cooked to retain their nutrient content.
Identifying Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Fat-soluble vitamins, on the other hand, are typically found in foods that contain fat. Good sources of these vitamins include dairy products, liver, oily fish, and fortified cereals. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, these vitamins are not easily destroyed by cooking methods, so they can be consumed in a variety of ways.
Checking Labels for Vitamins
Another way to identify whether a vitamin is water-soluble or fat-soluble is to check the label of a food or supplement. Water-soluble vitamins are typically listed as vitamin C and the B-complex vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, vitamin B6, folate, and vitamin B12). Fat-soluble vitamins, on the other hand, are listed as vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and vitamin K. By checking the label, you can determine which vitamins you are getting and adjust your diet or supplementation accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the classification of vitamins into water-soluble and fat-soluble is essential for maintaining good health. While both types of vitamins are necessary for the body to function properly, they have different properties and requirements for absorption and storage. By identifying which vitamins are water-soluble and which are fat-soluble, you can ensure that you are consuming a well-balanced diet that meets your nutritional needs.